Describe Two Leaf Modifications and Their Functions
During transpiration water evaporates from. It is present on both sides of the leaf and is called the upper and lower epidermis respectively.
Learn About Shapes And Modifications Of Leaf Chegg Com
Leaves are altered for defence storage reproduction support and to trap insects.

. The internal structure of the leaf is protected by the leaf epidermis which is continuous with the stem epidermis. Leaves are sometimes also converted into spines for defence example. The epidermis helps in the regulation of gas exchange.
However in a few plants leaves are modified to perform different functions. Leaf Structure and Function. Leaves modified for Reproduction.
Though the main function of leaves is to carry out photosynthesis in a lot of plants the modification of roots performs various functions. Most succulents have leaves modified-adapted for storing water. More specifically the leaves form a pitcher-like structure with a deep cavity filled with digestive liquids.
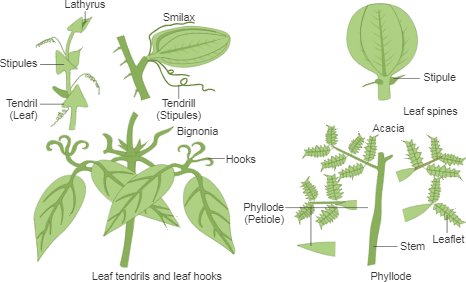
Entire leafLathyrus stipulesSmilax terminal leafletNaravelia Leaf tip Gloriosa Apical leafletPisum petioleClematis. B The leaves of pitcher plant are modified to form pitfall traps. They are of different types-Whole Leaf Tendrils - Whole leaf is modified into tendril.
The leaves of a pea plant are modified into tendrils that help the plant in climbing. A compound leaf has many leafletsmultiple leaf segments which are as a result when the lamina incision reaches the midrib. But Kalanchoe has leaves that have become modified to generate new plants.
In peas the terminal leaflet of the leaf has become modified into a tendril for climbing. A leaf must take in carbon dioxide from the surrounding air via pores called. Now up your study game with Learn mode.
Some of the modification of leaf tendrils are given below. Explain how various leaf modifications help plants. The leaves then curl inward and the network of trichomes forms a death-trap around the insect.
These help the plant in climbing. Understanding of the logic behind the varied forms of leaves is facilitated by a firm grasp of the precise functions a leaf must accomplish. A thin waxy layer that covers the upper epidermis of the leaf preventing the loss of water.
Therefore they become an important part of the plants. But in many plants the leaves are modified to perform some additional functions. The outermost layer of the leaf is the epidermis.
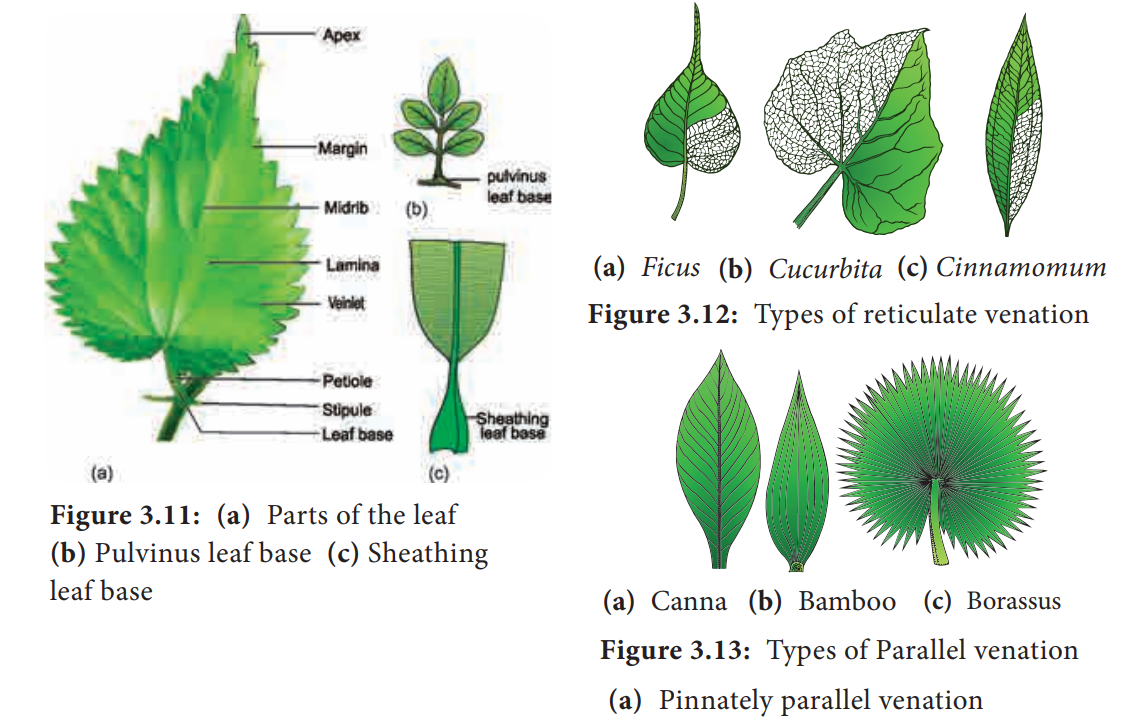
A single layer of clear cells that allows light to pass through and prevents the loss of water. Simple leaves possess only one lamina. Xylem moves water from roots to the leaves and phloem moves food from the leaves to the rest of the plant.
These are called as leaf modifications Some of the leaf modifications are. Botanists call the upper side the adaxial surface or adaxis and the lower side the abaxial surface or abaxis. Leaves are converted into tendrils for the purpose of climbing as seen in peas.
Thicsk waxy cuticle on the epidermis to prevent evaporation from leaf surface. The stem of the plant or the branches are modified to green thread-like leafless structures known as tendrils and are used for climbing. Leaves of certain insectivorous plants such as Venus fly trap pitcher plant are also modified leaves.
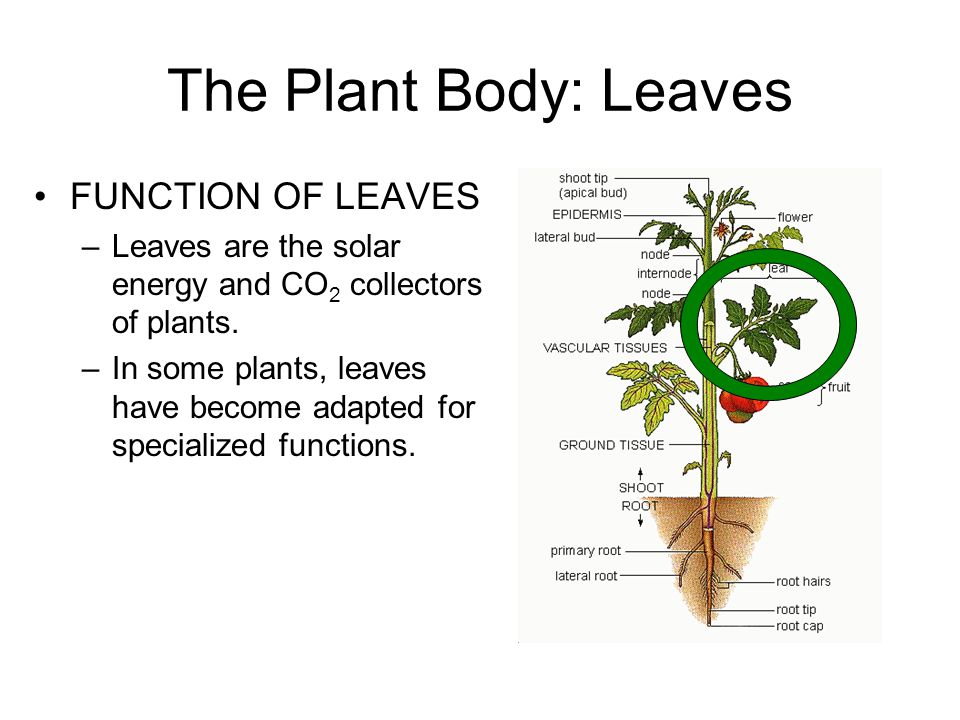
Reproductive leaves Produce adventitious plantlets which fall of the leaf and take root in the soil. The main function of a leaf is to produce food for the plant by photosynthesis. Water plants may have stomata on the tops of their leaves.
A leaf must capture sunlight for photosynthesis and as it does this it may also absorb a great deal of heat 2. Typically leaves are determinately growthed. The primary functions of leaf are photosynthesis and transpiration.
Tendrils can be subdivided into 4 types which are mentioned below. Cactus The fleshy leaves of onion and garlic store food. The functions of leaf modifications are.
Modifications of leaves can be of different types-1. Up to 24 cash back Leaves needles-shaped to reduce surface area for transpiration and to resist wind damage. The leaves are modified into slender wiry and.
The grow function and then die without sustaining new growth. They are unbranched and naked. In some plants leaves are modified into hook-like structures and help the plant to climb.
You just studied 10 terms. These tendrils can be both branched and unbranched and a scale leaf can be seen at the point of branching. The central leaf or mesophyll consists of soft.
Function Food synthesis gas exchange through stomata transpiration. The leaves in cactus are modified into sharp spines that act as an organ of defense. The main function of the leaves is to carry out the process of photosynthesis.
Paripinnate leaves of tamarind and imparipinnate leaves of roses are unipinnate as they have leaflets attached directly to the rachis. Leaf Tendrils - Leaf or leaf part are modified into tendril like structure for climbing. Chlorophyll the substance that gives plants their characteristic green colour absorbs light energy.
Leaf spines egZizyphus 4. Coiled structures called leaf. Sunken stomata to create high humidity and reduce transpiration.
The glandular secretions then begin digesting and engulfing the insect. In bi-pinnate leaves the rachis is branched and the leaflets are arranged pinnately on the secondary axes of the rachis as in the sensitive plant B.
Leaf Characteristic Features Functions Types Parts Of The Leaf
Leaves Form Function Ppt Video Online Download

8 Fun Science Activities For Kids About Leaves Science Activities For Kids Fun Science Science For Kids
No comments for "Describe Two Leaf Modifications and Their Functions"
Post a Comment